Adderall Detox Guide – Withdrawal Symptoms and Timeline
[three-fifths-first]
Adderall, a popular stimulant combining amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, is used primarily to treat attention hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and (less commonly) narcolepsy. The drug also appears on the Drug Enforcement Administration’s (DEA) list of highly controlled Schedule 11 substances. A recent study published in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry found Adderall abuse to be highest among 18 to 25 year olds, many of whom acquire the drug illicitly through family members and friends. More alarmingly, illicit use increased by 67 percent within the last decade — with emergency room visits rising 156 percent as a result.
[/three-fifths-first]
[two-fifths]
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Introduction to Adderall Detox
- Adderall Withdrawal Symptoms
- Adderall Withdrawal Timeline
- Inpatient Treatment for Adderall
- Outpatient Treatment for Adderall
- Can Adderall Detox Be Done at Home?
- Tapered vs. Cold Turkey
- Considerations for Adderall Detox
- Recovery Success and Aftercare Services for Adderall
[/two-fifths][clearfix]

Is Adderall ruining your life? Call: (855) 935-2871
ADDERALL WITHDRAWAL SYMPTOMS
The physical and psychological changes associated with chronic Adderall use vary dramatically, as do the accompanying withdrawal symptoms. A variety of clinical tools and objective measurements are used when assessing the severity of withdrawal symptoms upon admission into a detox program. The mildness or severity of symptoms, based upon specific scores, helps determine treatment goals including when Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) begins and optimal timelines for therapy.
Adderall withdrawal symptoms may include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Exhaustion
- Restlessness
- Mood swings
- Tremors
- Rapid heart rate
- Disordered thinking
- Psychosis
[/one-half-first]
[one-half]
- Irritability
- Anxiety
- Panic attacks
- Intense cravings
- Difficulty concentrating
- Increase in appetite
[/one-half][clearfix]
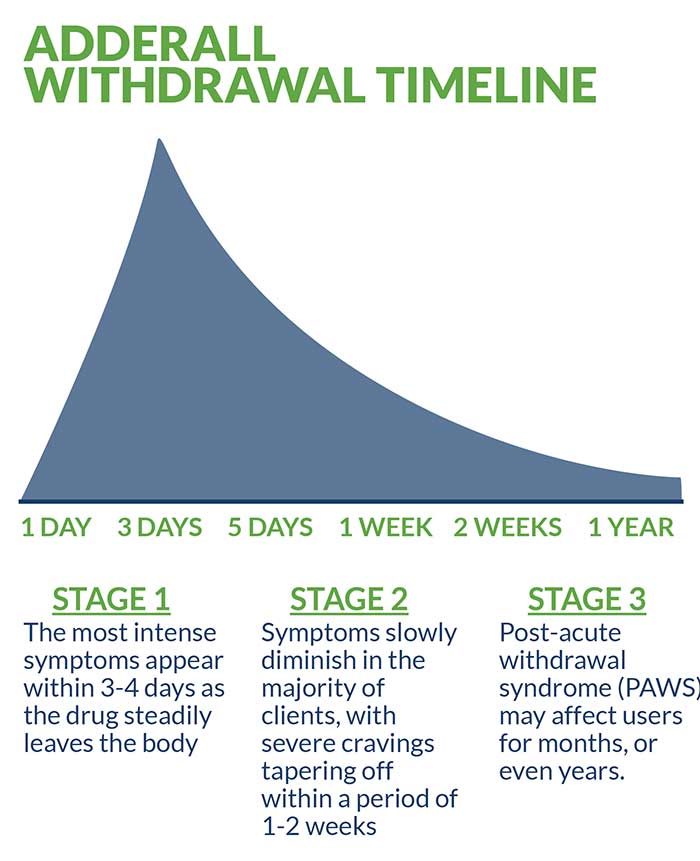
ADDERALL WITHDRAWAL TIMELINE
The prevention of precipitated withdrawal—the rapid and potentially dangerous onset of symptoms—is the primary treatment objective of medically supervised detox. Like any stimulant drug that creates dependency and addiction, there are considerable variables in the initial appearance of withdrawal symptoms. Typically, the most intense symptoms appear within three to four days as the drug steadily leaves the body. After this initial phase, symptoms slowly diminish in the majority of clients, with severe cravings tapering off within a period of one to two weeks.
While the acute phase of Adderall withdrawal is considered fairly rapid, lingering post-acute withdrawal syndrome (PAWS) may affect users for months, or even years. A multitude of factors including age, overall health and the severity and frequency of use all combine to determine the immediacy, intensity and duration of symptoms. Another factor invariably affecting withdrawal symptoms is drug longevity. Extended-release versions of Adderall take approximately 60 hours to leave the bloodstream and impact both short-term symptoms and lingering PAWS.
Adderall has a half-life of approximately 9-14 hours. This means that between 9-14 hours following dosage, approximately half of the drug remains in your system. Like most drugs, Adderall testing is frequently performed using hair, urine, saliva and blood samples. Adderall is detectable in urine between four and seven days, whereas hair samples can detect the drug for up to 90 days. Saliva and blood represent the middle of the testing range, with saliva detecting the drug in as little as 20 minutes following dosage and up to 48 hours. In blood testing, Adderall can be detected in as little as 12 hours following dosage and up to 24 hours.
INPATIENT TREATMENT FOR ADDERALL
Although numerous treatment options for Adderall detox exist, inpatient treatment in a residential facility is considered optimal. Frequently referred to as the industry “gold standard,” medically managed inpatient treatment offers a more comprehensive range of services and benefits. In addition to regular evaluation and assessment by a team of licensed medical professionals and clinicians, clients enjoy the added advantage of a safe, supportive environment where sobriety remains the top priority throughout their stay. Many reputable facilities also offer impressive ancillary benefits and services, including life and jobs skills coaching, alumni networking and ongoing aftercare services. More importantly, the 24/7 staff monitoring adds an additional blanket of security and proves invaluable to clients while navigating the various stages of withdrawal— many of which can be debilitating.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is an evidence-based protocol combining prescription medicine with behavioral and psychotherapy. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved pharmacological interventions form the cornerstone of treatment in many facilities. Once specific prescription needs are determined, a multitude of evidence-based therapies are incorporated into the treatment regimen in order to achieve maximum benefit. This regimen may include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavioral therapy (DBT), trauma-informed therapy, family therapy, motivational interviewing (MI), expressive and artistic therapies, and regular involvement in 12-Step recovery groups.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment
Like many addictions, Adderall addiction frequently occurs in tandem with anxiety or depression-related disorders. This phenomenon is known as “co-occurring” or “co-existing” disorders. In addition to the presence of co-occurring disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is often a precipitating factor involved in Adderall addiction and may be included in the treatment protocol. Evidence-based, FDA-approved medications including gabapentin, buspirone, pregabalin, and SSRIs (or “selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors”) are all examples of prescriptions commonly utilized in dual-diagnosis treatment.
OUTPATIENT TREATMENT FOR ADDERALL
Although outpatient treatment offers an affordable alternative to inpatient treatment, it is generally considered less comprehensive and effective. In the majority of outpatient settings, many of the same treatment methods are employed, but without the added benefit of 24/7 monitoring and intensive client supervision. The primary advantage associated with outpatient treatment is that it offers a degree of flexibility necessary for certain clients based upon their personal and/or professional needs.
CAN ADDERALL DETOX BE DONE AT HOME?
Due to the cumulative physiological and psychological effects of Adderall, self-guided detox in a home setting is never recommended. Once Adderall dependent, only licensed medical professionals and qualified clinicians can safely determine specific treatment needs and help reduce the dangers associated with withdrawal. Unfortunately—because Adderall is sometimes wrongly considered to be a relatively “safe” or “mild” drug— users may resort to self-treatment, a scenario that almost always leads to unfavorable outcomes, including relapse, and carries with it a host of unnecessary risks. For this reason, it is never recommended.
TAPERED VS COLD TURKEY
A tapered approach to detox is the most frequently utilized method. This allows for a carefully controlled medication regimen administered in a safe clinical setting. It should be noted that quitting any medication cold turkey runs the risk of triggering an extreme backlash, making the potential for relapse more likely and, in the process, jeopardizing health. Although not common, quitting Adderall cold turkey can lead to a trip to the emergency room, and even death.
CONSIDERATIONS/HOW TO DECIDE WHAT IS RIGHT FOR YOU
Many factors play a role in determining what is optimal for each client—with schedule, location, affordability, and insurance all contributing to the overall equation. Of all these factors, insurance is the most important in choosing an appropriate treatment for the majority of clients. Reputable facilities will be able to verify benefits prior to enrollment, with many clients receiving partial or total coverage. In cases where out-of-pocket costs are incurred, financial options including payment plans are discussed in addition to the possibility of scholarships, federal grants and/or other forms of aid. This helps ensure a relatively smooth, stress-free admission process.
RECOVERY SUCCESS AND AFTERCARE SERVICES FOR ADDERALL
Optimal treatment outcomes are achieved by following a multifactorial post-treatment approach. Although certain unforeseen factors help determine the likelihood of long-term sobriety, many can be controlled and maximized for increased success. A comprehensive aftercare plan should include ongoing medication management, random drug testing, one-on-one, and group therapy, life and job skills, a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and abstinence from social and environmental triggers associated with cravings and use.
For more about Adderall detox and recovery, check out these related articles:
- Dangers of Drug Detox at Home and Quitting Cold Turkey
- 5 Organs Damaged by Long-Term Adderall Abuse
- Millennials and Smart Drugs in the Workplace
- Common Forms of Prescription Drug Abuse and Their Dangers
Is Adderall ruining your life? Get help now
Sources:
Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. Adderall Misuse Rising Among Young Adults. February 16, 2016.
Columbia Graduate Science Journal. Addicted to Adderall. Volume 9. Spring, 2015.
Psychology Today. Will Adderall be the New Opioid Crisis? May, 2018.
Brigham Young University. Adderall abuse as final exam study aid “trending” among U.S. students. May, 2013.
Live Science. Adderall Abuse is a Growing Problem, Experts Warn. February, 2016.